Table of Contents
ToggleEngineers and electronics hobbyists often come across terms like VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and VBAT in datasheets and circuit schematics.But what do these abbreviations mean, and why are they critical in understanding a device’s power architecture? This article explores each term’s meaning, function, and differences to help you navigate modern electronics with ease.
Introduction to Power Supply Labels
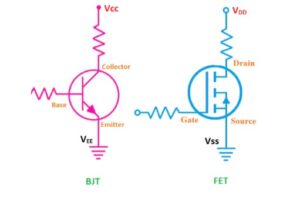
In integrated circuits (ICs) and printed circuit boards (PCBs), manufacturers use shorthand labels for power supply pins. These designations simplify schematics but can confuse beginners. The vcc full form stands for “Voltage at the Common Collector,” originating from bipolar junction transistor (BJT) circuits, while others like VDD and VSS stem from MOSFET-based designs.
What Does VCC Mean?
VCC Full Form and Its Origin
The vcc full form is “Voltage at the Common Collector.” It refers to the positive supply voltage connected to the collector of BJTs. For most logic circuits, VCC denotes the main positive voltage rail.
- Typical voltage levels: +3.3V, +5V, or +12V in digital systems
- Usage: Microcontrollers, TTL logic families, and power rails for BJTs
Differences Between VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and VBAT
To avoid confusion, let’s break down their functions and compare them.
| Label | Full Form | Type of Device | Voltage Polarity | Usage |
| VCC | Voltage at Common Collector | Bipolar Junction Transistor | Positive supply (+) | Powering logic circuits |
| VDD | Voltage at Drain | MOSFET | Positive supply (+) | Powering CMOS integrated circuits |
| VSS | Voltage at Source | MOSFET | Ground (0V) | Shared ground in circuits |
| VEE | Voltage at Emitter | BJT | Negative supply (-) | Used in op-amps or dual supplies |
| VBAT | Voltage at Battery | Any | Positive (battery voltage) | Backup power source in RTC modules |
This table clearly shows how each term applies to specific semiconductor technologies.
VDD and VSS: MOSFET-Centric Nomenclature
In MOSFET-based circuits, VDD is the positive voltage applied to the drain of NMOS transistors, while VSS represents the source voltage, often tied to ground.
- Example:A CMOS IC may use VDD = +3.3V and VSS = 0V
- Trend:As technology scales, VDD voltages have dropped from 5V to as low as 1.0V in advanced microprocessors.
VEE and VBAT: Specialized Roles
VEE: Negative Voltage Rail
- Use case:Op-amp circuits or analog ICs needing dual supplies
- Voltage range:Often -5V, -12V for symmetrical power
VBAT: Battery Voltage Input
- Powers real-time clocks (RTC), memory backup, or low-power circuits
- Common in devices where battery backup is essential during main power loss
Why Understanding These Terms Matters
Knowing the vcc full form and related terms helps engineers avoid critical design errors, especially when interfacing components from different logic families. A mismatch, like connecting a 5V VCC device to a 3.3V VDD system, can damage sensitive ICs.
Additionally, as IoT and wearable devices grow, understanding VBAT management for low-power operation is becoming increasingly relevant.
Practical Example: Microcontroller Power Pins
A popular microcontroller, the STM32F4 series, uses:
- VDD:3V for core and I/O supply
- VSS:Ground reference
- VBAT:8V-3.6V for RTC backup
Designers must ensure decoupling capacitors are placed near these pins to minimize noise.
Final Thoughts
The abbreviations VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS, and VBAT are more than just labels—they reflect the evolution of semiconductor technology. Whether you’re debugging a circuit or designing a new product, understanding these power terms is essential. Always check datasheets for pin functions and voltage levels to avoid costly mistakes.



-768x768.jpg)