Table of Contents
ToggleIn the world of electronics and electrical engineering, several abbreviations and terms are crucial for understanding how devices function. One of the most common terms you might come across is VDD. In this article, we will explore the VDD meaning, its role in circuits, and how it influences electronic device operation. By the end of this guide, you will have a solid understanding of what VDD means, its applications, and its significance in different types of electronics.
What is VDD Meaning?
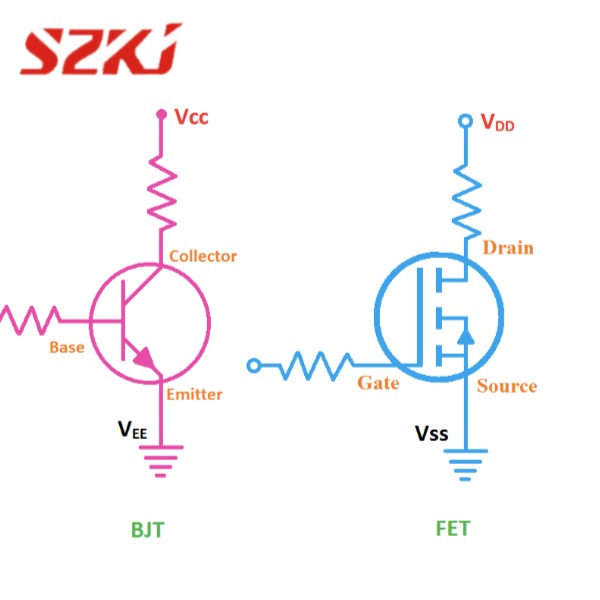
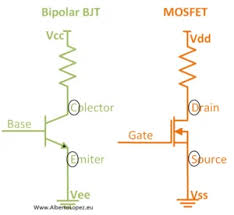
The term VDD stands for “Voltage Drain Drain” or “Voltage at Drain” in semiconductor terminology. It refers to the supply voltage that powers electronic circuits, especially in the context of transistors and integrated circuits (ICs). More specifically, VDD typically represents the positive voltage source for devices like field-effect transistors (FETs), MOSFETs, and other integrated components.
In simple terms, VDD meaning refers to the power supply voltage that is applied to the drain terminal of a transistor in most of the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) devices. It is crucial because it helps control the operation of the transistor, enabling it to perform its switching functions effectively. Without VDD, many electronic components wouldn’t operate.
VDD and Its Role in Electronic Circuits
The VDD meaning extends beyond just its definition; understanding how it functions in a circuit is key to mastering electronic designs. In a typical CMOS circuit, VDD is often the positive power supply connected to the drain of MOSFET transistors. This voltage allows current to flow between the source and the drain, controlling the flow of electrical signals.
In digital electronics, VDD is critical for logic gate operation. Logic gates, such as AND, OR, and NOT gates, use VDD to perform their fundamental functions. When the input signals of a gate are processed, VDD helps create a high or low output signal, which forms the building block for digital computation.
Importance in CMOS Technology
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) technology is a dominant method for constructing integrated circuits. In CMOS devices, VDD and VSS (ground) are the two essential power supplies. VDD serves as the positive voltage supply, while VSS represents the negative or ground reference point. The VDD meaning in this context is paramount because the voltage supplied to the drain of a transistor determines how the circuit will behave, either switching ON or OFF.
In a CMOS logic circuit, VDD is typically designed to be a fixed voltage, often 3.3V, 5V, or even higher depending on the specific design requirements. It ensures that the MOSFETs have enough potential to conduct current when required. Without proper VDD voltage, the transistors will not switch correctly, causing the circuit to fail.
Common Applications of VDD in Electronics
Understanding the VDD meaning becomes much clearer when you see its applications in real-world devices. VDD is essential in various areas of electronics, such as:
- Microprocessors and Microcontrollers:These devices rely on stable VDD supply voltages to function efficiently. The power supplied by VDD controls the performance of the processor, ensuring proper execution of instructions.
- Analog Circuits:In operational amplifiers (op-amps) and other analog ICs, VDD provides the necessary power for amplification. Without the correct VDD voltage, the op-amp would not be able to amplify signals properly.
- Power Management Systems:Many power management ICs require a constant VDD voltage to regulate and distribute power throughout the system. These ICs are often found in devices like smartphones, laptops, and consumer electronics.
- Battery-Powered Devices:In devices like handheld gadgets and wearables, VDD plays a crucial role in ensuring that the battery delivers sufficient power to keep the device functioning.
- Communication Systems:Transceivers and other communication ICs also rely on VDD to maintain the integrity of signal transmission and reception.
VDD in Modern Electronics: Trends and Innovations
As electronics continue to evolve, the VDD meaning has also adapted to meet the needs of modern technology. For example, with the push towards energy-efficient devices, lower VDD values are being used to reduce power consumption. This is particularly relevant in the context of mobile devices and IoT (Internet of Things) systems, where power efficiency is paramount.
Additionally, as circuit designs become more complex, the demand for VDD regulation has increased. Voltage regulators, such as low-dropout regulators (LDOs), are used to provide stable VDD supply voltages even when the input voltage fluctuates. This ensures that sensitive electronics receive a consistent power supply, preventing malfunction.
Conclusion: Why Understanding VDD is Crucial
To wrap up, the VDD meaning is not just an abbreviation; it represents a key component of electronic circuit design. Whether you are designing integrated circuits, working with microprocessors, or developing consumer electronics, understanding VDD is essential for ensuring proper functionality. From digital logic circuits to battery-powered devices, VDD plays a pivotal role in powering the electronics that drive modern technology.
By now, you should have a solid grasp of VDD meaning and its significance in the broader context of electronics. Whether you’re an engineer, hobbyist, or just curious about electronics, knowing the role of VDD will help you better understand how devices work and how circuits are designed.